GALILEO
Return to main
Galileo Table of Contents Page.
The Galileo Energetic Particles Detector
Galileo EPD Handbook
Chapter 1. Instrument Summary
Geometric Factor Calculation for the EPD LEMMS Telescope
Source: Andreas Lagg, Galileo EPD Science Team Meeting, March 1998
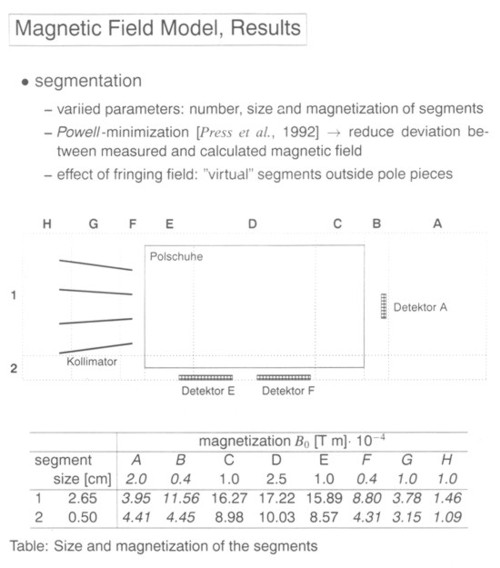
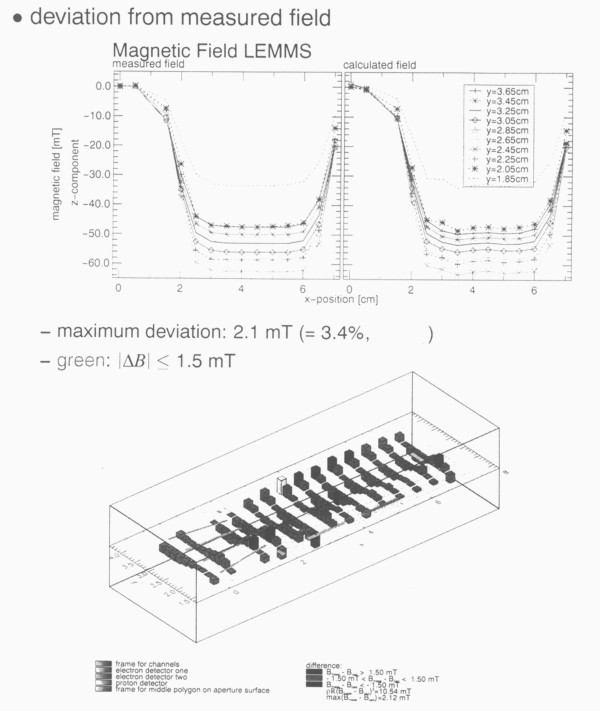
3. Results
Geometric factors, electrons:
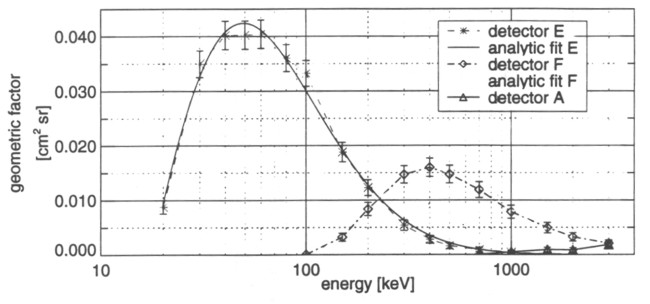
|
GF[E0,E1](γ)[cm2 sr] · 103 |
||||||
| Channel | Detector | E0 - E1 (keV) | γ=0 | γ=1 | γ=3 | γ=5 |
| E0 | E | 15-29 | 15.23 | 13.09 | 9.04 | 5.81 |
| E1 | E | 29-42 | 38.61 | 38.42 | 38.01 | 37.60 |
| E2 | E | 42-50 | 40.23 | 40.23 | 40.23 | 40.23 |
| E3 | E | 55-93 | 37.54 | 37.86 | 38.49 | 39.04 |
| F0 | E | 93-188 | 22.55 | 23.97 | 26.71 | 28.95 |
| F0 | F | 93-188 | 2.81 | 2.39 | 1.63 | 1.05 |
| F1 | F | 174-304 | 11.15 | 10.72 | 9.85 | 9.05 |
| F2 | F | 304-527 | 15.44 | 15.48 | 15.52 | 15.53 |
| F3 | F | 527-884 | 11.80 | 12.01 | 12.43 | 12.80 |
| Detector A | 527-884 | 0.10 | 0.08 | 0.06 | 0.04 | |
(assuming power law distribution: I(E) ∝ E-γ)
Return to Galileo EPD Handbook Table of Contents Page.
Return to main
Galileo Table of Contents Page.
Return to Fundamental
Technologies Home Page.
Updated 8/23/19, Cameron Crane
QUICK FACTS
Manufacturer: The Galileo Spacecraft
was manufactured by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory,
Messerschmitt-Bölkow-Blohm, General Electric, and the
Hughes Aircraft Company.
Mission Duration: Galileo was planned to have a mission duration of around 8 years, but was kept in operation for 13 years, 11 months, and 3 days, until it was destroyed in a controlled impact with Jupiter on September 21, 2003.
Destination: Galileo's destination was Jupiter and its moons, which it orbitted for 7 years, 9 months, and 13 days.
Mission Duration: Galileo was planned to have a mission duration of around 8 years, but was kept in operation for 13 years, 11 months, and 3 days, until it was destroyed in a controlled impact with Jupiter on September 21, 2003.
Destination: Galileo's destination was Jupiter and its moons, which it orbitted for 7 years, 9 months, and 13 days.



