GALILEO
Investigation of the Magnetosphere of Ganymede with Galileo's Energetic Particle Detector
Ph.D. dissertation by Shawn M. Stone, University of Kansas,
1999.
Copyright 1999 by Shawn M. Stone. Used with permission.
M1 07:11:13 Figures
 |
Figure B22 (A) Simulated M1 and real (Re) rate profile for the feature G7-07:11:13 of channel E1 normalized to 90º of pitch. (B) The pitch and phase angles as calculated from the look direction of the EPD detector and the appropriate magnetic field vector R for real and S for simulated. |
 |
Figure B23 (A) Simulated M1 and real (Re) rate profile for the feature G7-07:11:13 of channel E3 normalized to 90º of pitch. (B) The pitch and phase angles as calculated from the look direction of the EPD detector and the appropriate magnetic field vector R for real and S for simulated. |
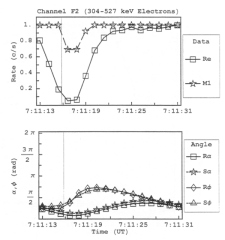 |
Figure B24 (A) Simulated M1 and real (Re) rate profile for the feature G7-07:11:13 of channel F2 normalized to 90º of pitch. (B) The pitch and phase angles as calculated from the look direction of the EPD detector and the appropriate magnetic field vector R for real and S for simulated. |
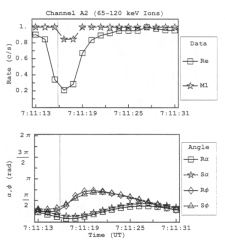 |
Figure B25 (A) Simulated M1 and real (Re) rate profile for the feature G7-07:11:13 of channel A2 normalized to 90º of pitch. (B) The pitch and phase angles as calculated from the look direction of the EPD detector and the appropriate magnetic field vector R for real and S for simulated. |
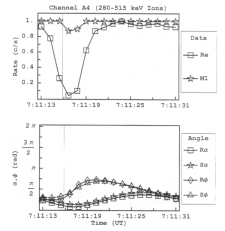 |
Figure B26 (A) Simulated M1 and real (Re) rate profile for the feature G7-07:11:13 of channel A4 normalized to 90º of pitch. (B) The pitch and phase angles as calculated from the look direction of the EPD detector and the appropriate magnetic field vector R for real and S for simulated. |
 |
Figure B27 (A) Simulated M1 and real (Re) rate profile for the feature G7-07:11:13 of channel A6 normalized to 90º of pitch. (B) The pitch and phase angles as calculated from the look direction of the EPD detector and the appropriate magnetic field vector R for real and S for simulated. |
Return to dissertation table of contents page.
Return to main
Galileo Table of Contents Page.
Return to Fundamental
Technologies Home Page.
Updated 8/23/19, Cameron Crane
QUICK FACTS
Manufacturer: The Galileo Spacecraft
was manufactured by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory,
Messerschmitt-Bölkow-Blohm, General Electric, and the
Hughes Aircraft Company.
Mission Duration: Galileo was planned to have a mission duration of around 8 years, but was kept in operation for 13 years, 11 months, and 3 days, until it was destroyed in a controlled impact with Jupiter on September 21, 2003.
Destination: Galileo's destination was Jupiter and its moons, which it orbitted for 7 years, 9 months, and 13 days.
Mission Duration: Galileo was planned to have a mission duration of around 8 years, but was kept in operation for 13 years, 11 months, and 3 days, until it was destroyed in a controlled impact with Jupiter on September 21, 2003.
Destination: Galileo's destination was Jupiter and its moons, which it orbitted for 7 years, 9 months, and 13 days.



