Investigation of the Magnetosphere of Ganymede with Galileo's Energetic Particle Detector
Ph.D. dissertation by Shawn M. Stone, University of Kansas,
1999.
Copyright 1999 by Shawn M. Stone. Used with permission.
6.4.1 Feature G2-19:08:51 (continued)
The results for extended bounce mode with the addition of scattering are presented in Figures 6.115 through 6.118 for model M2 energy channels E3 and F2. In this case, the feature fills in with increasing scattering coefficient. The important fact here is that scattering is necessary to recover the feature. Figures 6.119 through 6.121 present the correlation plots for model M2 channels E1, E3, and F2 respectively. From these plots it can be seen that the scattering coefficient is a function of energy. Figures 6.122 through 6.124 present the correlation plots for model M1 channels E1, E3, and F2 respectively.
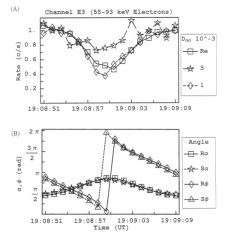 |
Figure 6.115 (A) Simulated M2 and real (Re) rate profile for feature G2-19:08:51 of channel E3 normalized to 90º of pitch. The simulated runs are done in extended bounce mode with scattering included. (B) The pitch (a) and phase (f) values of the particles as measured by the EPD detector. |
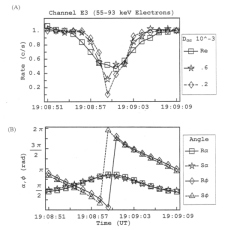 |
Figure 6.116 (A) Simulated M2 and real (Re) rate profile for feature G2-19:08:51 of channel E3 normalized to 90º of pitch. The simulated runs are done in extended bounce mode with scattering included. (B) The pitch (a) and phase (f) values of the particles as measured by the EPD detector. |
 |
Figure 6.117 (A) Simulated M2 and real (Re) rate profile for feature G2-18:56:31 of channel F2 normalized to 90º of pitch. The simulated runs are done in extended bounce mode with scattering included. (B) The pitch (a) and phase (f) angles are computed from the look direction of the EPD detector and the appropriate magnetic field vector R for real and S for simulated.. |
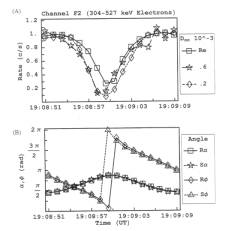 |
Figure 6.118 (A) Simulated M2 and real (Re) rate profile for feature G2-18:56:31 of channel F2 normalized to 90º of pitch. The simulated runs are done in extended bounce mode with scattering included. (B) The pitch (a) and phase (f) angles are computed from the look direction of the EPD detector and the appropriate magnetic field vector R for real and S for simulated. |
 |
Figure 6.119 Correlation of feature G2-19:08:51 with simulated M2 E1 data for varying values of Daa. This graph shows that the scattering coefficient with the highest correlation is Daa = 2 x 10-3 s. |
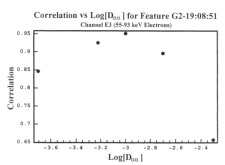 |
Figure 6.120 Correlation of feature G2-19:08:51 with simulated M2 E3 data for varying values of Daa. This graph shows that the scattering coefficient with the highest correlation is Daa = 1 x 10-3 s. |
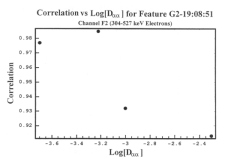 |
Figure 6.121 Correlation of feature G2-19:08:51 with simulated M2 F2 data for varying values of Daa. This graph shows that the scattering coefficient with the highest correlation is Daa = 6 x 10-4 s. |
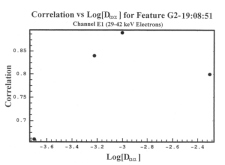 |
Figure 6.122 Correlation of feature G2-19:08:51 with simulated M1 E1 data for varying values of Daa. This graph shows that the scattering coefficient with the highest correlation is Daa = 2 x 10-3 s. |
 |
Figure 6.123 Correlation of feature G2-19:08:51 with simulated M1 E3 data for varying values of Daa. This graph shows that the scattering coefficient with the highest correlation is Daa = 2 x 10-3 s. |
 |
Figure 6.124 Correlation of feature G2-19:08:51 with simulated M1 F2 data for varying values of Daa. This graph shows that the scattering coefficient with the highest correlation is Daa = 2 x 10-3 s. |
Next: 6.4.2 Feature G2-19:10:51
Return to dissertation table of contents page.
Return to main
Galileo Table of Contents Page.
Return to Fundamental
Technologies Home Page.
Updated 8/23/19, Cameron Crane
QUICK FACTS
Mission Duration: Galileo was planned to have a mission duration of around 8 years, but was kept in operation for 13 years, 11 months, and 3 days, until it was destroyed in a controlled impact with Jupiter on September 21, 2003.
Destination: Galileo's destination was Jupiter and its moons, which it orbitted for 7 years, 9 months, and 13 days.



