GALILEO
Return to main
Galileo Table of Contents Page.
The Galileo Energetic Particles Detector
Galileo EPD Handbook
Chapter 1. Instrument Summary
Numerical Calculation of Three-Dimensional Electron and Proton Trajectories in the Galileo EPD LEMMS Sensor Assembly (continued)
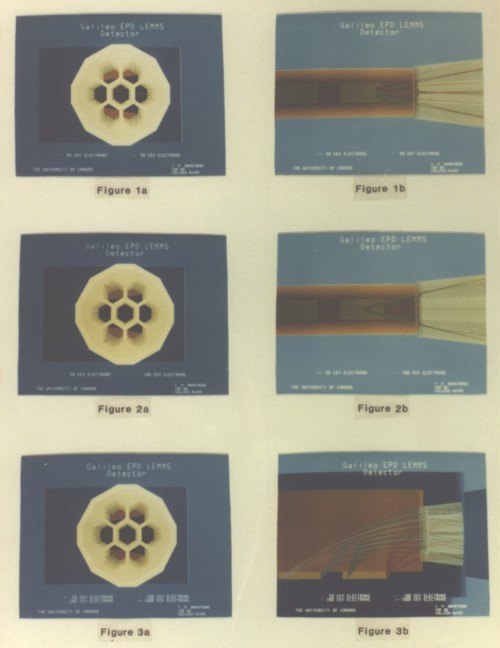
Photos 1a and 1b: 50
keV electron trajectories for off-midplane impact.
a.) Front view (Y-Z plane); b.) Top view (X-Z plane).
Colors: white - aperture stack; orange - pole pieces; green
- electron detectors (E,F)
Photos 2a and 2b: 50
and 100 keV electron trajectories for midplane impact on
detector E.
a.) Front view (Y-Z plane); b.) Top view (X-Z plane)
Photos 3a and 3b: 50,
100, 200, and 1000 keV electron impacts on the midplane of
detectors E and F.
a.) Front view (X-Z plane); b.) Side view (X-Y plane)
Next: Conclusion
Return to Galileo EPD Handbook Table of Contents Page.
Return to main
Galileo Table of Contents Page.
Return to Fundamental
Technologies Home Page.
Updated 8/23/19, Cameron Crane
QUICK FACTS
Manufacturer: The Galileo Spacecraft
was manufactured by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory,
Messerschmitt-Bölkow-Blohm, General Electric, and the
Hughes Aircraft Company.
Mission Duration: Galileo was planned to have a mission duration of around 8 years, but was kept in operation for 13 years, 11 months, and 3 days, until it was destroyed in a controlled impact with Jupiter on September 21, 2003.
Destination: Galileo's destination was Jupiter and its moons, which it orbitted for 7 years, 9 months, and 13 days.
Mission Duration: Galileo was planned to have a mission duration of around 8 years, but was kept in operation for 13 years, 11 months, and 3 days, until it was destroyed in a controlled impact with Jupiter on September 21, 2003.
Destination: Galileo's destination was Jupiter and its moons, which it orbitted for 7 years, 9 months, and 13 days.