The Galileo Energetic Particles Detector
Galileo EPD Handbook
Chapter 2. EPD Software
Energetic Particle Detector Experiment Flight Software System Documentation (continued)
Source: H. Malcom, July 30, 1982
2.0 SOFTWARE SYSTEM OVERVIEW (continued)
Major Software Modules
The major software modules that are included in the Galileo EPD software system are listed below:
Real Time Executive
Initialization
LEMMS PHA Spectrum Accumulation and Compression
Real Time Interrupt Handler
Memory checksum
Ten Real Time Interrupt Interval Service Routines
Data System and Motor Controller Command Queue Loader
Command Decoder and Executor
CMS PHA Input Routine
Rate Channel Data Compression and Packing Routine
Subcommutated Housekeeping Routine
Figure 2.2 shows the hierarchical relationship between the various modules within the EPD software system:
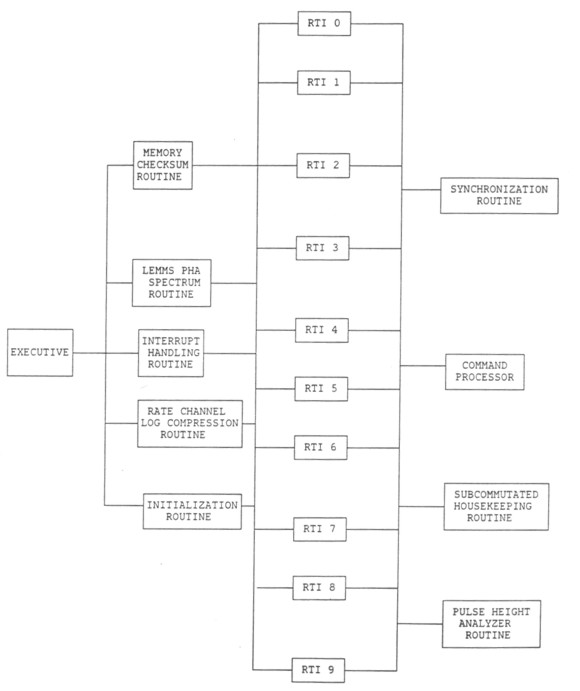
The real time executive, in addition to performing system initialization, accumulates and log-compresses LEMMS PHA spectra and computes a memory checksum of a subset of ROM that can be specified by a group of data system commands. Accumulation of LEMMS PHA spectra and the computation of memory checksums are performed as background tasks--that is, in between tasks when the system is responding to interrupts. The executive, upon receiving an interrupt, saves the state of the software system and transfers control to one of ten real time interval interrupt handlers. The appropriate interrupt handler is determined by a real time interval (TRI) counter that is maintained by the executive.
Each of the ten interrupt handlers carries out the tasks that are scheduled for the corresponding RTI by invoking one or more subroutines for each of the tasks to be performed.
Next: 3.0 Microprocessor System Hardware Overview
Return to EPD Flight Software System Documentation table of contents page.
Return to Galileo EPD Handbook Table of Contents Page.
Return to main
Galileo Table of Contents Page.
Return to Fundamental
Technologies Home Page.
Updated 8/23/19, Cameron Crane
QUICK FACTS
Mission Duration: Galileo was planned to have a mission duration of around 8 years, but was kept in operation for 13 years, 11 months, and 3 days, until it was destroyed in a controlled impact with Jupiter on September 21, 2003.
Destination: Galileo's destination was Jupiter and its moons, which it orbitted for 7 years, 9 months, and 13 days.



